How Its Made
Ceramic 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a sophisticated process that blends traditional ceramic techniques with modern 3D printing technology. This innovative method has revolutionized the ceramic industry, allowing for the creation of intricate and unique designs that were previously impossible to achieve.
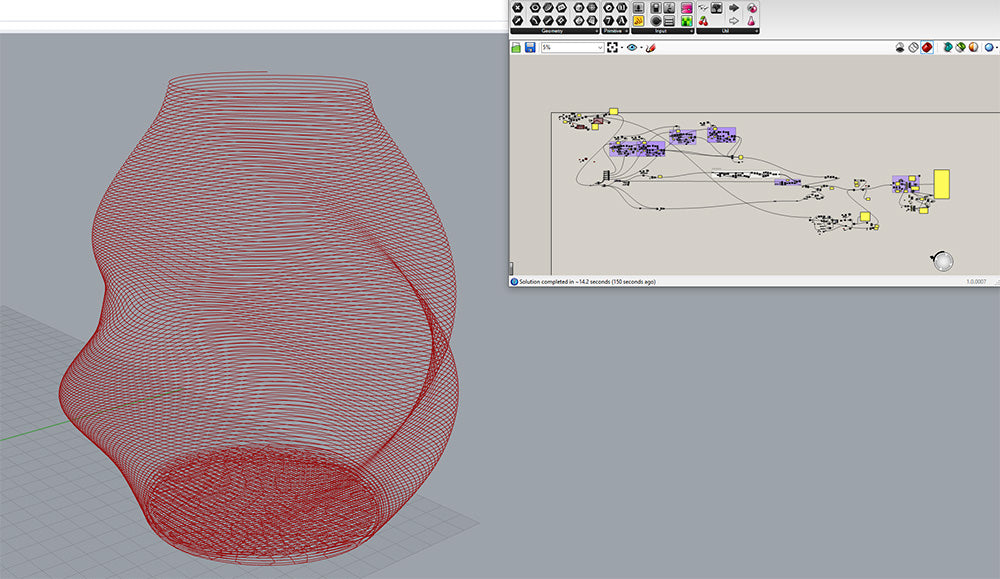
Digital Modeling
The process begins with creating a digital model using 3D design software. Designers can create intricate and precise designs that would be challenging to achieve with traditional methods. This digital model is then sliced into layers, generating a set of instructions for the 3D printer.
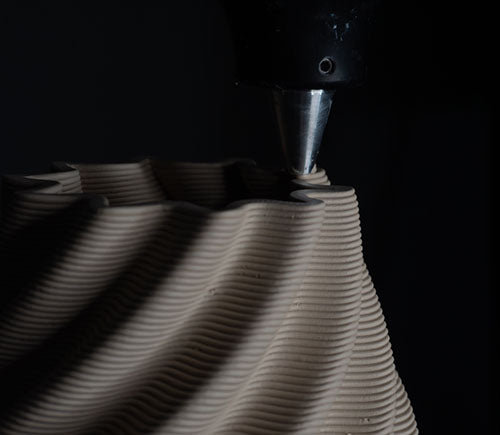

3D Printing
The prepared clay is loaded into the 3D printer. The printer extrudes the clay layer by layer according to the digital design. This process allows for high precision and the creation of complex shapes and patterns. Each layer is carefully deposited and shaped to build up the final object gradually.
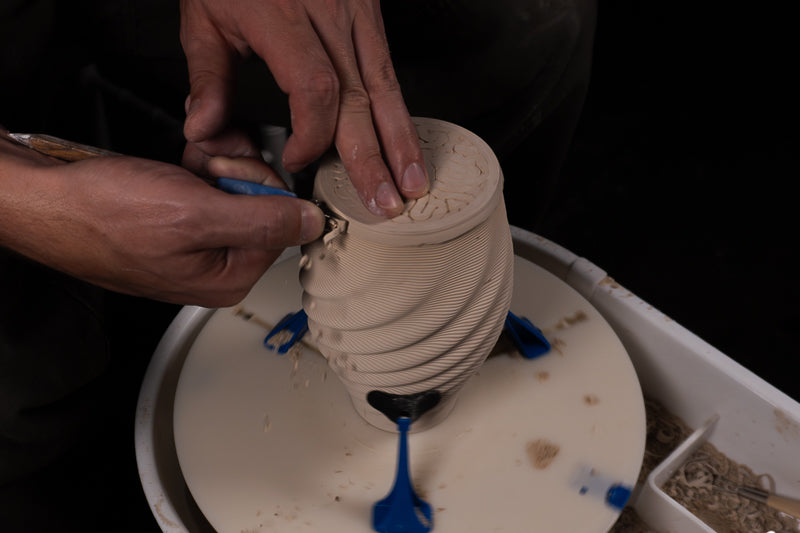

Trimming
Ceramic trimming involves refining a leather-hard piece on a potter's wheel. The process includes removing excess clay, defining the shape, and adding details like foot rings. This is done using various tools to achieve a smooth, precise finish. Trimming enhances the piece's aesthetics and functionality by ensuring balanced weight and a polished look.
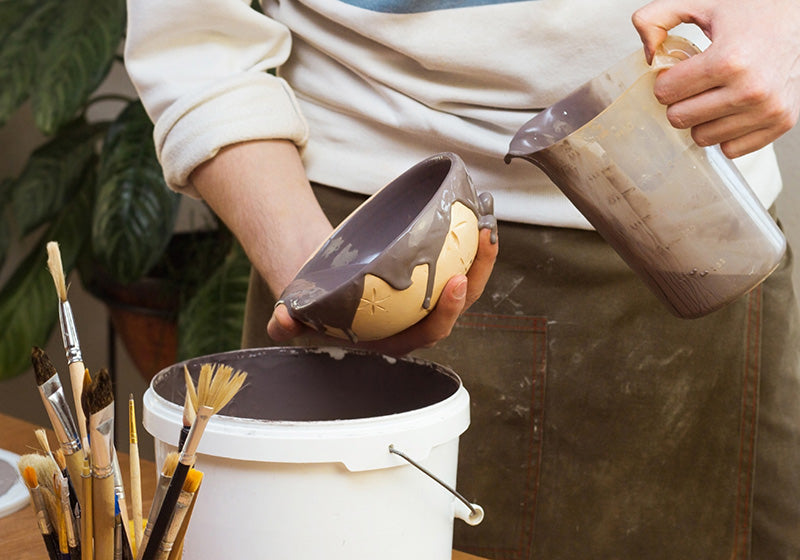

Glazing
The glazing process for ceramics starts with cleaning and, if necessary, sanding the bisque-fired piece. Glaze is then applied via dipping, brushing, spraying, or pouring. After air drying, the piece is fired in a kiln at 1200°C, where the glaze melts and bonds. This results in a durable, decorative, non-porous finish suitable for functional and aesthetic use.
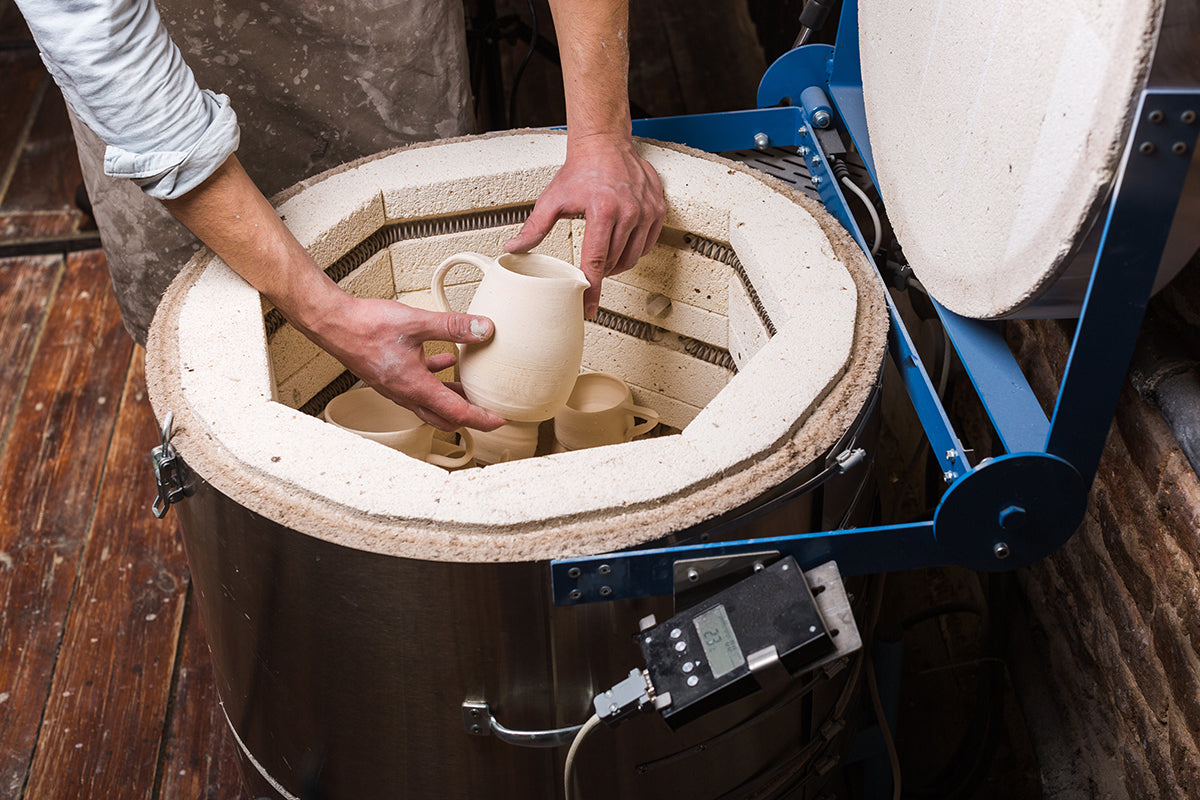

Firing
Kiln firing is a complex and essential process in ceramics, requiring careful control of temperature and timing to achieve the desired results. The combination of bisque and glaze firing produces robust, beautiful, and functional ceramic objects.
